Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watanabe, Kazuki; Kimura, Norimichi*; Okada, Jumpei; Furuuchi, Yuta; Kuwana, Hideharu*; Otani, Takehisa; Yokota, Satoru; Nakamura, Yoshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2023-010, 29 Pages, 2023/06
The Krypton Recovery Development Facility reached an intended technical target (krypton purity of over 90% and recovery rate of over 90%) by separation and rectification of krypton gas from receiving off-gas produced by the shearing and the dissolution process in the spent fuel reprocessing at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) between 1988 and 2001. In addition, the feasibility of the technology was confirmed through immobilization test with ion-implantation in a small test vessel from 2000 to 2002, using a part of recovered krypton gas. As there were no intentions to use the remaining radioactive krypton gas in the krypton storage cylinders, we planned to release this gas by controlling the release amount from the main stack, and conducted it from February 14 to April 26, 2022. In this work, all the radioactive krypton gas in the cylinders (about 7.1 10
10 GBq) was released at the rate of 50 GBq/min or less lower than the maximum release rate from the main stuck stipulated in safety regulations (3.7
GBq) was released at the rate of 50 GBq/min or less lower than the maximum release rate from the main stuck stipulated in safety regulations (3.7 10
10 GBq/min). Then, the equipment used in the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas and the main process (all systems, including branch pipes connected to the main process) were cleaned with nitrogen gas. Although there were delays due to weather, we were able to complete the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas by the end of April 2022, as originally targeted without any problems such as equipment failure.
GBq/min). Then, the equipment used in the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas and the main process (all systems, including branch pipes connected to the main process) were cleaned with nitrogen gas. Although there were delays due to weather, we were able to complete the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas by the end of April 2022, as originally targeted without any problems such as equipment failure.
Matsushima, Ryotatsu; Sato, Fuminori; Saito, Yasuo; Atarashi, Daiki*
Proceedings of 3rd International Symposium on Cement-based Materials for Nuclear Wastes (NUWCEM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2018/10
At TRP, LWTF was constructed as a facility for processing low radioactive liquid waste and solid waste generated at TRP, and a cold test is been carrying out. In this facility, initially, nitrate waste liquid after separation of nuclides generated with treatment of low radioactive liquid waste was to be solidified by using borate. However, at present, it is necessary to decompose the nitrate in the liquid waste to reduce the environmental burden. For the reason, as a plan to replace the nitrate with the carbonate and to make it as a cement based encapsulation, we are studying for the introduction of the facility. Currently, as a cement solidification technology development for this liquid waste, we are studying the application of cement material based on blast furnace slag (BFS) as a main component. In this report, we show the results of the test conducted on the actual scale (200 L drum can scale).
 2016.10
2016.10Horigome, Kazushi; Taguchi, Shigeo; Ishibashi, Atsushi; Inada, Satoshi; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
JAEA-Technology 2017-008, 14 Pages, 2017/05
The plutonium solution had been converted into MOX powder to mitigate the potential hazards of storage plutonium solution such as hydrogen generation at the Plutonium Conversion Development Facility. The plutonium conversion operations had been started in April, 2014, and had been finished in July, 2016. With respect to the samples taken from the conversion process, about 2,200 items of plutonium/uranium solutions and MOX powders had been analyzed for the operation control in the related analytical laboratories at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant. This paper describes the reports on analytical activities and related maintenance works in the analytical laboratories conducted from December, 2015 to October, 2016.
 2015.12
2015.12Horigome, Kazushi; Suzuki, Hisanori; Suzuki, Yoshimasa; Ishibashi, Atsushi; Taguchi, Shigeo; Inada, Satoshi; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
JAEA-Technology 2016-026, 21 Pages, 2016/12
In order to mitigate potential hazards of storage plutonium in solution such as hydrogen generation, conversion of plutonium solution into MOX powder has been carried out since 2014 in the Plutonium Conversion Development Facility. With respect to the samples taken from the conversion process, about 3500 items of plutonium/uranium solutions and MOX powders have been analyzed for the operation control in the related analytical laboratories at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant. This paper describes the reports on analytical activities and related maintenance works in the analytical laboratories conducted from April 2014 to December 2015.
; ; *; *; *; *; *
JNC TN8440 2000-013, 179 Pages, 2000/04
The plutonium conversion development facility (PCDF) has been operated for 17 years and about 12 tons plutonium-uranium mixed oxide (MOX) powder has been converted since operation started in 1983. The first maintenance program for aging of apparatus was carried out from 1993 to 1994. The calcination-reduction fumace, liquid waste evaporator had been dismantled and renewed. The second maintenance program was carried out form 1998 to 1999. The microwave ovens, powder blender, ventilation control panel and so on were dismantled and renewed. Large volume radioactive wastes were generated during this maintenance such as the furnace, the filter casings and glove boxes. These wastes were too large to be packed into the waste container and these wastes were polluted by MOX powder unfixed on these surface. SO cutting and packing operation for these wastes and recovery of MOX powder from them were carried out. In this report, the method of this cutting and packing operation, the radioactive exposure to the operators in this operation, the estimation of nuclear material quantity migrated to filters, the evaluation of re-floating factor of radioactive material, etc. were discussed.
Shirai, Nobutoshi; ; ; Shirozu, Hidetomo; Sudo, Toshiyuki; Hayashi, Shinichiro;
JNC TN8410 2000-006, 116 Pages, 2000/04
Criticality limits for equipments in Tokai Reprocessing Plant which handle fissile material solution and are under shape and dimension control were reevaluated based on the guideline No.10 "Criticality safety of single unit" in the regulatory guide for reprocessing plant safety. This report presents criticality safety evaluation of each equipment as single unit. Criticality safety of multiple units in a cell or a room was also evaluated. The evaluated equipments were ones in dissolution, separation, purification, denitration, Pu product storage, and Pu conversion processes. As a result, it was reconfirmed that the equipments were safe enough from a view point of criticality safety of single unit and multiple units.
; ; *; *; Masaki, Toshio; Kobayashi, Hiroaki; *
PNC TN8410 98-041, 185 Pages, 1998/02
The 9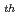 test of Joule-Heated Cylindrical Electrode Melter - Engineering Scale (JCEM-E9 Test) was carried out from June to July 1996, as a part of the development program on an advanced glass melter. The principal purpose of the test was to estimate the effect of noble metal on operation of the melter with simulated high-level liquid waste. Besides, we also evaluated the basic operational characteristics with corrosion of electrodes, qualities of produced glass etc. JCEM-E is an electric glass melter with an internal electrode and an external electrode in a subsidiary furnace. The internal electrode is a rod inserted in the center of external electrode that is a cylindrical tank. The glass is melted by conducting electric current through the molten glass between the internal and external electrodes. The subsidiary furnace is composed of multi-layer refractories inside a metallic casing and is equipped with the resistance heaters. Melting surface area is 0.35 m
test of Joule-Heated Cylindrical Electrode Melter - Engineering Scale (JCEM-E9 Test) was carried out from June to July 1996, as a part of the development program on an advanced glass melter. The principal purpose of the test was to estimate the effect of noble metal on operation of the melter with simulated high-level liquid waste. Besides, we also evaluated the basic operational characteristics with corrosion of electrodes, qualities of produced glass etc. JCEM-E is an electric glass melter with an internal electrode and an external electrode in a subsidiary furnace. The internal electrode is a rod inserted in the center of external electrode that is a cylindrical tank. The glass is melted by conducting electric current through the molten glass between the internal and external electrodes. The subsidiary furnace is composed of multi-layer refractories inside a metallic casing and is equipped with the resistance heaters. Melting surface area is 0.35 m that i8 approximately half of 0.66 m
that i8 approximately half of 0.66 m of TVF melter. In the test, 13 batches of glass was produced and total weight of produced glass was 3663kg. As a result, The maximum processing rate of JCEM-E with simulated HLLW including noble metals was 4.20
of TVF melter. In the test, 13 batches of glass was produced and total weight of produced glass was 3663kg. As a result, The maximum processing rate of JCEM-E with simulated HLLW including noble metals was 4.20 5.60kg/h, and decreased to less than 80 percent compared with JCEM-E8 Test with non-noble metals HLLW. It was considered that the decrease of the rate arose from concentration of current due to non-uniform distribution of noble metals in molten glass. Judging from the balance of feed and draining, and as a consequence of the observation inside the melter after the test, the draining of noble metals from the nozzle was good. As for the quality of glass produced in the test, properties of concern were comparable with those of standard glass of TVF.
5.60kg/h, and decreased to less than 80 percent compared with JCEM-E8 Test with non-noble metals HLLW. It was considered that the decrease of the rate arose from concentration of current due to non-uniform distribution of noble metals in molten glass. Judging from the balance of feed and draining, and as a consequence of the observation inside the melter after the test, the draining of noble metals from the nozzle was good. As for the quality of glass produced in the test, properties of concern were comparable with those of standard glass of TVF.
; ; Miyazaki, Hitoshi; ; Tanimoto, Kenichi; Terunuma, Seiichi
PNC TN9420 95-011, 13 Pages, 1994/10
None
; Miyazaki, Hitoshi; ; Tanimoto, Kenichi; Terunuma, Seiichi
PNC TN9420 94-010, 103 Pages, 1994/04
None